Tagged: search engine marketing
Our 2026 Digital Marketing Checklist
- by Luke Thiessen
What we’re planning for, bracing for, and watching for this year in the world of digital marketing
By Luke Thiessen, Director
I used to call it “Mythical January.”
In a previous job where I led a nonprofit communications team, we would talk all year – especially as we neared and weathered the busy holiday season – about Mythical January. It was the time when we all expected to be able to sit back, catch up on all of the projects that fell by the wayside throughout the year, and plan for the year ahead.
But every year, without fail, we would reach Mythical January, and two things would happen. First, we would realize the list of things we left for January was longer than we could possibly tackle. And second, some opportunity or emergency would come up that would shake us from our leisurely catch-up session and set us right back on the hamster wheel of work that wouldn’t stop again until after Christmas.
So this year, I thought I’d kick off the Starling blog with some planning advice and insights to help you make the most of your Mythical January – whatever that looks like for you.
We’re going to look at some of the challenges, opportunities, and emerging technologies that we expect will warrant our attention this year. I hope this helps you plan your 2026 digital marketing and strategize for the year to come!
A.I. Everything
You know we had to start here. Sometimes we love it, sometimes we hate it, but it’s not going away, so might as well embrace it.
We still believe human-created content is king, and will continue to be this year, but we as marketers know that AI is making its way into more facets of our work – so it’s important to understand what’s happening.
One area where we’re watching AI closely is in ad delivery. Many of our main digital ad channels are integrating AI into how they do targeting and placements, including Meta and Google. So for 2026, we are watching the data closely to see if and how these tools actually impact results, what the best use cases are, and if there are any issues we need to be watching for.
Another major area of AI integration we are watching is in search. This impacts a few things, from how we approach SEO on our websites and blogs to PPC (Pay-Per-Click) advertising in search. So far, this has had a smaller and slower impact than many marketers feared, but AI is still changing the way we approach search engine marketing. So for 2026, we are continuing to invest in the tools and strategies that continue to deliver results, but we are also bracing for a future where much of this could change.
We are also watching the AI regulatory landscape this year, as 2025 already brought some significant international developments which could hint at what’s to come. Regulation in the EU (as well as China and some parts of the U.S.) is forcing disclosures for AI-generated content and AI-assisted technologies. There are also active lawsuits in Canada which are likely to impact things here, as our government has indicated it’s watching for court decisions before enacting any AI regulation.
Alternative Search
This overlaps somewhat with what we’re watching in AI, but two major shifts are happening in search right now that cannot be ignored: chatbots as search, and social media as search.
AI chatbots are quickly taking market share from traditional search engines, as more people type their queries directly into ChatGPT or other AI tools. The line here blurs a little, as the chatbots appear to be getting at least some of their results directly from Google (not to mention Gemini, one of the most popular chatbots, is a Google product). However, it is a significant trend that is changing how many users engage with search.
Social media is doing something similar, especially among younger users who are typing queries directly into the (mostly AI-powered) search bars within social media apps. This makes SEO more complicated in a lot of ways, but at minimum reinforces the importance of having good strategic copy across all of your social media content.
Short-Form Video
Video has been the king of content for a while now, but its importance just keeps growing. TikTok shows no signs of slowing down, and virtually every other platform is scrambling to keep users on board by prioritizing similar video feeds.
For 2026, we are watching the pace of this shift to video-first, looking at more efficient and cost-effective ways of embracing video content, and evaluating how this should fit into overall strategy for our clients.
Authenticity
In the age of AI slop and automated marketing, we (as well as many other experts) believe that authenticity will only become more important in 2026.
Authenticity has always been one of our core values at Starling Social, but we are seeing increasing evidence that it makes for more effective digital marketing. Real people want to see and hear real people in their social feeds, and that applies to advertising too.
The challenge here is that video is often the most expensive and/or labour-intensive content to make, whether for organic social or ads. However, making something that feels authentic can also mean making something less polished and more natural – so there is also opportunity here for marketers with smaller budgets and modest tools.
Niche Platform Advertising
Perhaps less of a trend and more of a personal project, something I’m trying to watch and do more of in 2026 is marketing on niche platforms.
You might not think of Reddit or LinkedIn as niche (both boast huge user numbers), but their advertising programs are barely a fraction of the size of Meta and Google. However, both have invested significantly in the quality of their ad business recently, and can deliver great results for a good price if done well. Targeting and placements naturally work differently here than on Meta or Google, and they are both home to strong niche communities of users, creating advertising opportunities you just can’t get elsewhere.
Getting Professional Help
Overall, it seems the world of digital marketing just keeps getting more challenging and complex – and in 2026 the pace of change has become almost dizzying. But that’s why we’re here.
If you could use help navigating any of this – from adapting your advertising strategy for AI, to creating more video content, to trying something new with your digital marketing – get in touch to book a discovery call today.
What's an Entity First SEO Strategy and How to Build One?
- by Alyson Shane
“Entity search” “might just be one of the most important SEO tactics you’ve never heard of!
This (somewhat) obscure term has become something we’ve been focusing on here at Starling Social since Google updated its topics application program interface (API) back in June of this year.
This update to Google’s most comprehensive and powerful deep learning algorithms means that marketers and businesses need to be thinking more deeply about semantic search than ever before.
If you’re new to terms like “semantic search” and “entity SEO” don’t worry! Today we’re going to dig into what these two terms mean, and how you can leverage them to help customers find your business.
What’s Semantic Search?
Semantic search describes a search engine’s efforts to generate the most accurate results on the search engine results page (SERP) by using algorithms to understand search intent, query context, and the relationship between the words being used.
Or to put it another way: semantic search is a search engine’s attempts to understand natural language the way a person would.
What is Entity Search?
Back in the day, a search was performed almost exclusively by typing words (keywords) into a search engine, but now 40 - 50% of all searches are conversational, meaning that they’re done through smartphones, Alexa, Google Home, etc.
This change is why search engines have put so much energy into understanding the context and intent behind a search query. As a result, search has evolved from keywords, to “entities”.
“Entities” are expressions that a search engine can understand without ambiguity, regardless of the language being used. This can include:
- A person’s name
- A numerical expression
- A place
- An object
- An event
- A concept

Let’s look at an example: the search query “what’s the cheapest price for an AirBnB in Toronto?”
Here’s how a search engine would understand the query:
- What: A concept (question qualifier)
- Cheapest: A numerical expression (lowest cost)
- Price: Numerical expression
- AirBnB: Organization
- Toronto: Location
By connecting these entities, search engines can understand both the search query, as well as the intent behind it.
Once these areas are understood, a search engine will try to find the most relevant information about the “entities” in the query by scanning content on the web and using AI to sort and present it to the user. This is called “entity/semantic search”.
The Difference Between Entity SEO and Traditional SEO
In traditional SEO, web pages are ranked on “scores” based on relevance, authority, and the number of backlinks from other websites.
Entity SEO focuses on showing the most useful information based on entities, facts associated with those entities and questions related to them.
What
The topic of the search query and what a user expects to find when they search for that topic. This sounds similar to traditional SEO and keywords, but semantic search takes a different approach.
Let’s think back to the example above: how many ways could someone ask the same question? Would it be asked differently in other languages?
Making sure your content is as comprehensive as possible and offers credible information about the topic, and covering as many related topics as possible, is how you can optimize your content for entity SEO.
Why
This describes the intent behind the search. What is the person looking to find out?
Are they considering and comparing options?
Are they looking for directions?
To make a decision?
To complete a transaction?
Using a combination of “what” and “why” will allow you to create content that’s SEO friendly and caters to your customers at every stage of their buying journey, so creating content around these topics and interconnecting them can help your page show up on a SERP more often.
How
Nowadays, how a search was performed is almost as important as what’s being searched for, so consider how your audience might want to consume the information they’re hoping to find.
Video, images, bulleted lists, hours of operation, FAQs and question and answer sections, and more are all excellent ways to create entity SEO-friendly content for your site.
The Four Outcomes Your Content Should Accomplish
The five outcomes you want to accomplish are:
1. Discoverability. Make sure your content is “discoverable” by search engines and by customers at different stages of their buyer’s journey.
2. Relevancy. Your content needs to meet your searcher’s needs and have as much info as possible.
3. User-friendly. Your content needs to be easy to read and understand.
4. Engaging. Engaging content encourages readers to take the desired goal (learn something, sign up, fill out a form, etc.)
Creating content that’s relevant, topical, and increases “discoverability” means keeping these elements in mind:
- The content should be personalized. Readers should feel like it was written for them, specifically.
- The content must tell a story. It needs to be engaging and capture readers’ attention.
- The content should be scannable. It needs to include headers, sub-headers, and elements like bulleted lists to make skimming easier.
- It must include images. These both break up the text, make things clearer, and offer more SEO optimization opportunities.
- The content must be mobile-friendly. According to Statista, 55.79% of all web traffic in Q1 2022 came from mobile devices, so make sure your content is readable on smaller screens.
How to Align Your Content With Entity First SEO
Before we talk about how to align your content, let’s take a quick look at how search engine priorities, algorithms, needs, and results have changed over time:
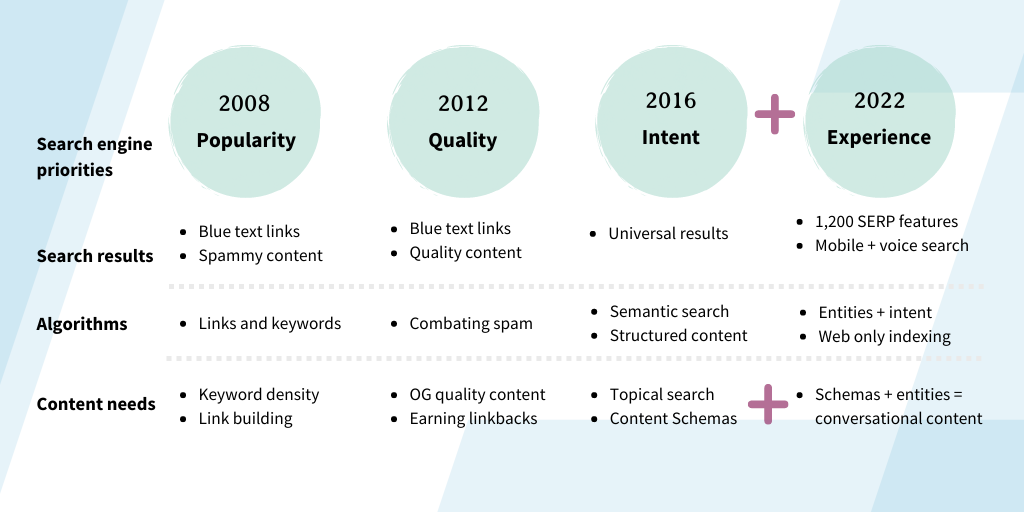
Like we said before: the way people are searching is changing, and the shift to searches performed through “screenless” devices means that the AI powering search engines is trying to replicate how humans think and speak.
If you’re wondering how you can tailor your SEO strategy to match how search engines have evolved, here’s how:
Consider Your Website Schema
This is a bit wonky, so stay with us: schema markup (also known as structured data) is the language of search engines. It was introduced by Google in 2011 as a way of helping search engines display more relevant results to users.
Web schemas are basically words or “shared vocabulary” that help refine searches and display more relevant results to the user.
Here’s an example: you and your friends want to go camping in Red Deer, Alberta… but when you try to perform a search, a bunch of results for red deer the animal come up. This is because Google didn't have context to understand that you wanted information on the city, not the animal.
So when you’re considering the content to write and the metadata to add to various pages on your site, make sure to consider the schema vocabulary to include, and the most relevant pages to include it on.
Consider the Market Opportunity for your Keywords
Use an in-depth keyword research tool (our fav is SEMRush) and do research into how different keywords in your industry are performing.
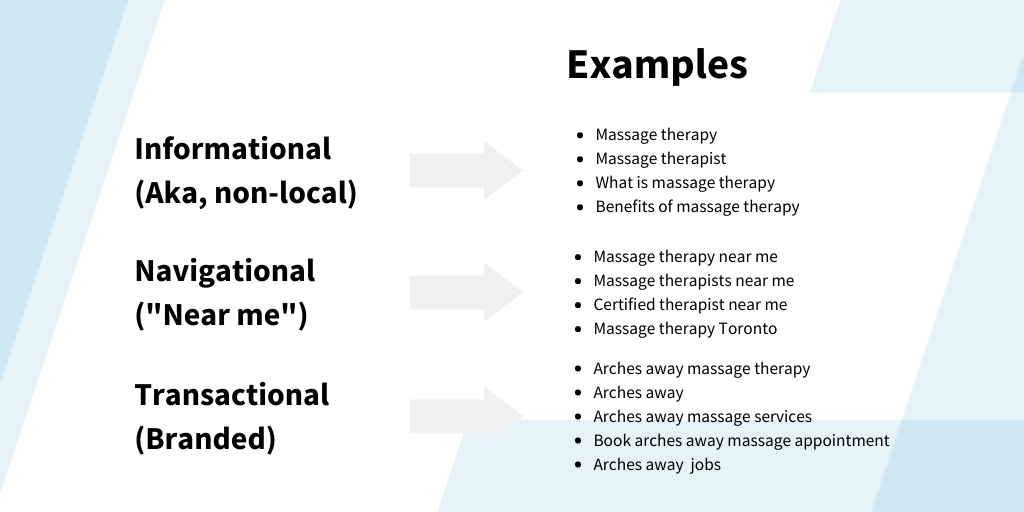
Then, map your content based on three factors:
1. Informational
2. Navigational
3. Transactional
Here’s an example of what that could look like:
Identify Topic Gaps
Once you’ve identified your high-priority keywords and the best pages to use them on, cross-reference those findings against topics and entities covered by other high-ranking websites.
Some things to cross-reference against your own site include:
- Image alt tags (here’s two easy ways to check)
- Headings
- Lists
- Metadata (here’s how to do that)
Update Your Web Pages
Once you’ve identified what other high-ranking sites are doing, it’s time to compare against the pages on your own site and start identifying the areas where you can start adding in more content and schema-focused keywords.
Some areas you’ll want to focus on updating and optimizing include:
- Meta Keywords Attribute. A series of keywords you deem relevant to the page in question.
- Title Tag. This is the text you’ll see in the SERP and at the top of your browser. Search engines view this text as the “title” of your page.
- Meta Description Attribute. A brief description of the page.
- Meta Robots Attribute. An indication to search engine crawlers (robots or “bots”) as to what they should do with the page.
More info on these topics can be found in this handy article from WordStream.
Protip: if your site is hosted on WordPress, the Yoast SEO tool is a great plugin that can help you optimize all these elements!
Optimize Your SEO for Entity Search: Recap
SEO is more about just the content on your page (though that’s important, too) — you need to consider the page layouts, how they link to one another, design elements, entity coverage, and schema.
To make this easier for yourself, think about the main pages on your site as “spokes” in a wheel, the other relevant pages that link back to it as the “spokes” in that wheel.
To recap, if you want to optimize your site for entity first SEO, take these steps:
- Consider your website schema
- Do research on your target keywords
- Identify topics on other high-ranking sites
- Identify content gaps between those sites and your own
- Update your pages with content, headers, metadata, etc.
Staying up-to-date with the latest SEO trends is easy! Just subscribe to our weekly digital marketing newsletter for the latest articles, resources, and insights.

